Your Questions
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT BREAST AGENESIS
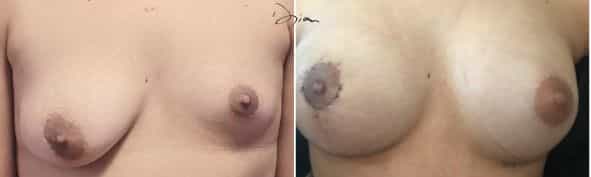
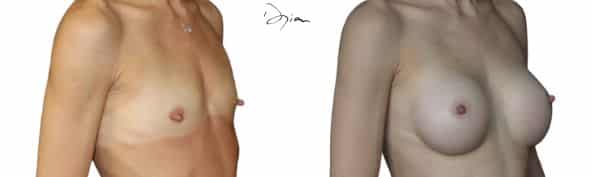
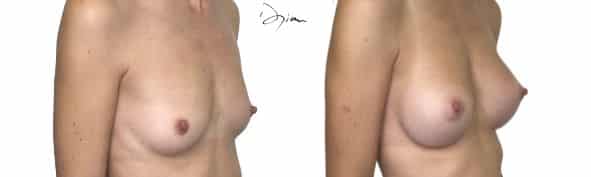
Breast agenesis, definition and difference with hypoplasia or hypotrophy?
Mammary agenesis refers to the total or partial absence of a mammary gland. Hypoplasia refers to a gland that is present but underdeveloped. Hypotrophy refers to a breast that is too small for its morphology.
These conditions can only be distinguished by clinical examination and imaging.
At what age should treatment be considered?
Intervention is only envisaged’after the end of growth, around 17 or 18 years of age. In some cases, hormonal treatment may be discussed beforehand if the deficit is diagnosed during puberty. In adults, only reconstructive surgery can restore lasting volume.
What is the average recovery time after surgery for missing breasts?
Full recovery takes about a month. Pain is moderate and scars discreet. Find out more about convalescence after breast augmentation: stages, duration and advice, see our dedicated article.
How much does breast augmentation cost?
The cost varies according to the technique used and the complexity of the case. Reconstruction by implant or lipofilling can cost from 4,000 to 7,000 euros. If the agenesis is recognized as a malformation, part of the cost may be reimbursed by the Assurance Maladie and the mutuelle.
How is coverage provided by Social Security, and what prior steps are required?
The covered by Social Security for a breast agenesis depends on a prior agreement obtained after a prior agreement request (DEP). The surgeon establishes a precise diagnosis, draws up a medical report detailing the malformation (total breast aplasia, severe asymmetry or tuberous breasts) and attaches standardized photos. This file is sent to the CPAM's medical advisor, together with an estimate and the planned surgical coding. The response time is 15 days The absence of a reply is tantamount to tacit agreement. In the event of agreement, the operation is recognized as reconstructive surgery and may be reimbursed in full or in part, depending on the severity and the technique used (implant, lipofilling, flap). Extra fees and related costs may be covered by the mutual insurance company, subject to presentation of notification of agreement.
Do breasts reconstructed by lipofilling evolve over time like natural breasts?
Yes, breasts reconstructed by lipofilling evolve in a similar way to natural breasts. The autologous fat injected integrates with existing tissues and reacts in the same way as they do to variations in weight, hormonal cycles or aging. Slight volume resorption may occur in the first few months, but the result remains stable thereafter. This prosthesis-free technique offers a supple, natural and long-lasting result, provided you maintain a stable body weight after the procedure.
IN THESE SECTIONS
TO DR. DJIAN